Have you ever felt a deep, nagging pain in your hip that won’t go away? It could be more than just soreness a herniated disc might be the culprit.
This common spinal condition can cause severe hip pain, disrupting daily life and limiting mobility. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is the first step to finding relief.
A herniated disc hip pain can cause significant hip pain.
This condition occurs when the soft tissue inside a spinal disc pushes out through its tough exterior. The herniation can press on nearby nerves, leading to discomfort in the hip and surrounding areas.
Causes of a Herniated Disc Hip Pain
- Age-Related Wear and Tear: As people age, spinal discs lose water content, making them less flexible and more prone to rupture.
- Injury or Trauma: Accidents or sudden impacts can damage spinal discs, leading to herniation.
- Repetitive Strain: Repeated bending, lifting, or twisting motions can weaken the spinal discs over time.
- Poor Posture: Sitting or standing with poor posture increases pressure on the spine, which may lead to disc problems.
- Genetics: Some individuals are more likely to develop herniated discs due to inherited traits.
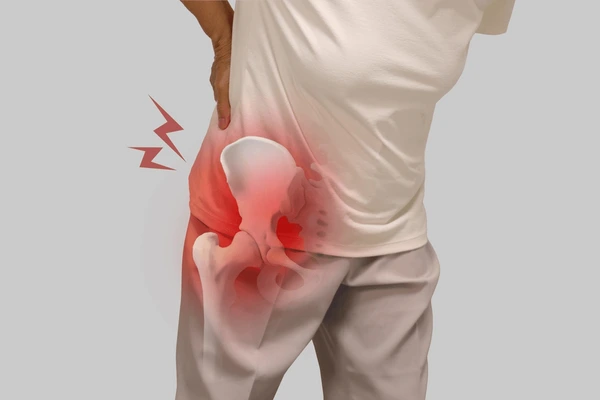
How a Herniated Disc Causes Hip Pain
The spinal nerves exit the spine and travel to various parts of the body, including the hips. When a disc herniates, it can compress these nerves, leading to pain in the hip area. This pain may feel sharp, burning, or like a deep ache. In some cases, the pain extends down the leg, a condition known as sciatica.
Symptoms Associated with Herniated Disc Hip Pain
- Localized Pain: Discomfort may occur in the lower back and radiate to the hip.
- Numbness or Tingling: Affected nerves may cause tingling sensations in the hip or leg.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the hip or leg can result from nerve compression.
- Limited Mobility: Pain and stiffness may restrict movement.
- Worsened Pain with Movement: Activities like bending, sitting, or lifting may increase discomfort.
Diagnosis of a Herniated Disc
Doctors use several methods to diagnose a herniated disc:
- Physical Examination: The doctor checks for pain points, reflexes, and strength in the affected areas.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans provide detailed images of the spine to confirm disc herniation.
- Nerve Tests: Electromyography (EMG) measures nerve activity to identify compressed nerves.
Treatment Options for Herniated Disc Hip Pain
- Rest and Activity Modification:
- Avoid activities that worsen the pain.
- Gentle movements and stretching can help maintain flexibility.
- Physical Therapy:
- Exercises strengthen the back and core muscles.
- Stretching improves flexibility and reduces nerve pressure.
- Pain Medications:
- Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen or acetaminophen reduce inflammation and pain.
- Prescription medications may be used for severe pain.
- Hot and Cold Therapy:
- Ice packs reduce swelling and numbness.
- Heat pads relax muscles and improve blood flow.
- Chiropractic Care:
- Gentle spinal adjustments may relieve nerve pressure and improve mobility.
- Injections:
- Cortisone injections reduce inflammation around the affected nerve.
- Surgery:
- If conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary to remove the herniated portion of the disc.
Preventing Herniated Disc and Hip Pain
- Maintain Proper Posture:
- Keep your spine aligned when sitting, standing, and lifting objects.
- Exercise Regularly:
- Strengthen your core and back muscles to support the spine.
- Include stretching exercises to improve flexibility.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting:
- Use your legs instead of your back when lifting heavy objects.
- Stay Active:
- Prolonged inactivity can weaken spinal support muscles.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Excess weight puts additional pressure on the spine.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if:
- Pain is severe and persistent.
- Numbness or weakness interferes with daily activities.
- Bladder or bowel control issues occur, as these may indicate a serious condition.
Conclusion
Herniated discs can cause hip pain, affecting daily life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments helps manage this condition effectively. Simple preventive measures and timely medical care can reduce the risk and improve quality of life.
